FIRST LAW
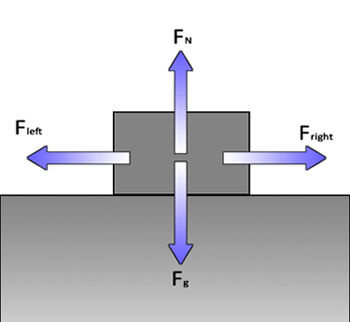
SECOND LAW
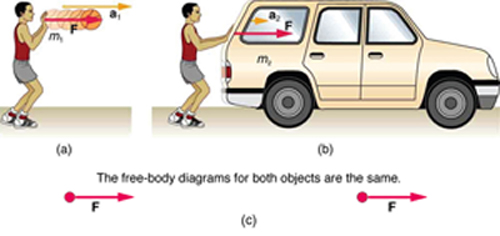
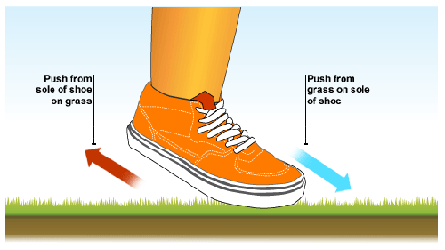
THIRD LAW



Newton's First Law
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced
FORCE.
There are two parts to this statement.One that predicts the behavior of stationary objects and the other that predicts the behavior of moving objects.
Newton's Second Law
States that if a NET FORCE acts on an object, it will cause an ACCELERATION of that object. The law addresses the cause and effect relationship between
FORCE and motion commonly stated as F = ma, where m is the proportionality constant (MASS). FORCE is measured in SI units of newtons, abbreviated N.
Newton's Third Law
States that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, if one object exerts a FORCE on a second object, the second exerts an equal and oppositely directed FORCE on the first one.